Answer (1 of 15) This question asks how nonseed plants reproduce, nowhere in the question is it asking about plants that can produce by cloning, grafting, or sporulating which also produce by seeding The nonseed plants are bryophytes Mosses, Apomixis is a form of asexual reproduction in some species of grasses The parent plant produces seeds without fertilization Fragmentation is another form of asexual reproduction It involves new plants growing from small parts of the parent plant that fall to the ground For example, animals or the wind can break stems or leaves off plants Spores are reproductive cells in plants;

What Are The Non Seed Plants With Examples Garden Bagan
Seed reproduction examples
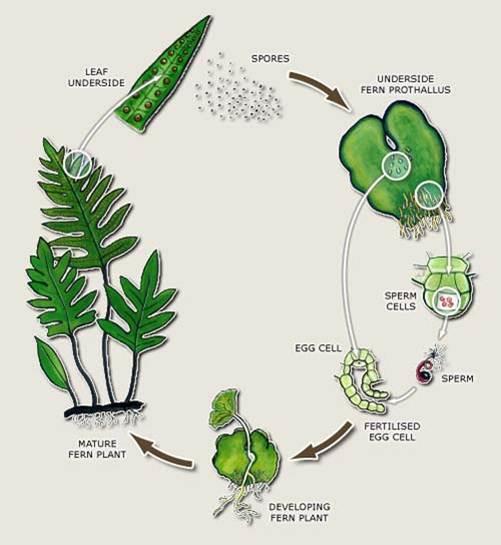
Seed reproduction examples-Although some plants are more reliable from seed and a few plants are "true" from seed, these are exceptions to the rule • When grown from seed, plants must grow through a juvenile stage and become mature enough to reproduce This generally takes from 315 years for most fruiting plants • Seed propagation is generally used by plant Plant reproduction without seeds Not every plant grows from a seed Some plants, like ferns and mosses, grow from spores Other plants use asexual vegetative reproduction and grow new plants from rhizomes or tubers We can also use techniques like grafting or take cuttings to make new plants Rights University of Waikato




Reproductive Systems And Evolution In Vascular Plants Pnas
The seed contains the embryo covered by the seed coat Cotyledon present in the seed helps in the nourishment of the developing baby plant on germination of the seed Learn more about Vegetative Propagation here Questions For You Q1 Which of the following statements is/are true for sexual reproduction in plants? Angiosperm, any of about 300,000 species of flowering plants, the largest and most diverse group in the plant kingdom Angiosperms are vascular seed plants in which the ovule is fertilized and develops into a seed in an enclosed ovary Learn about angiosperm characteristics, evolution, and importancePlant reproduction is the production of new offspring in plants, which can be accomplished by sexual or asexual reproduction Sexual reproduction produces offspring by the fusion of gametes, resulting in offspring genetically different from the parent or parentsAsexual reproduction produces new individuals without the fusion of gametes, genetically identical to the parent plants
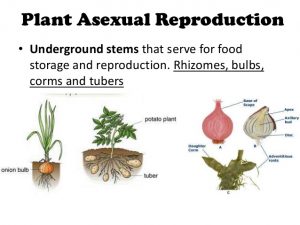
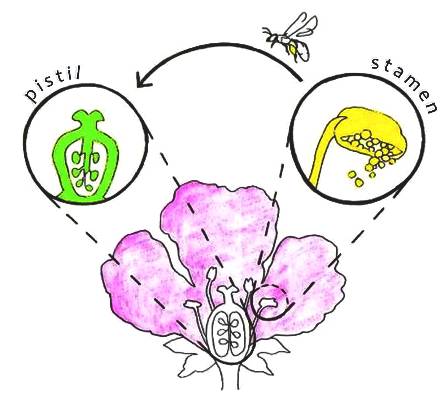
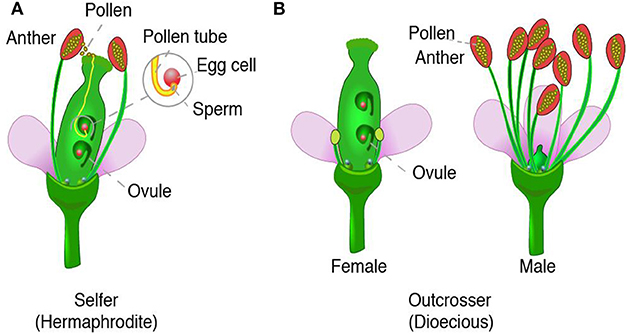
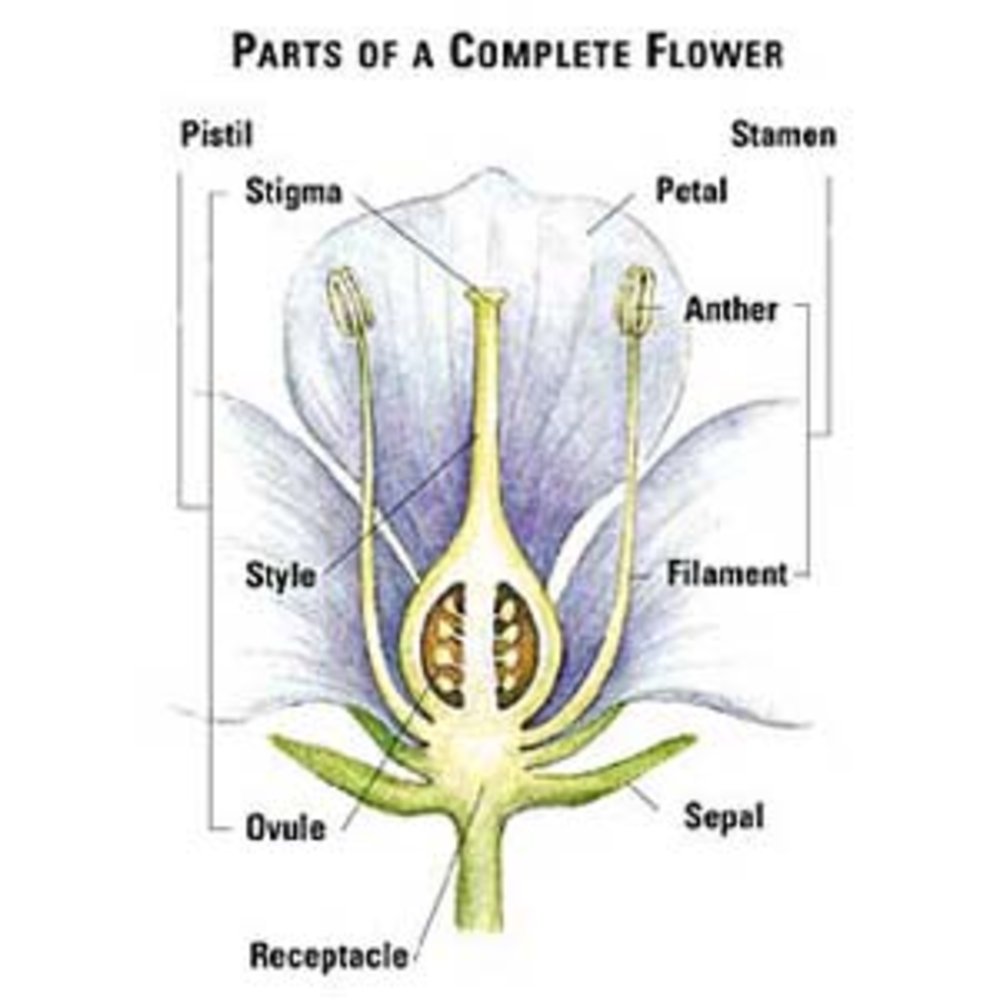
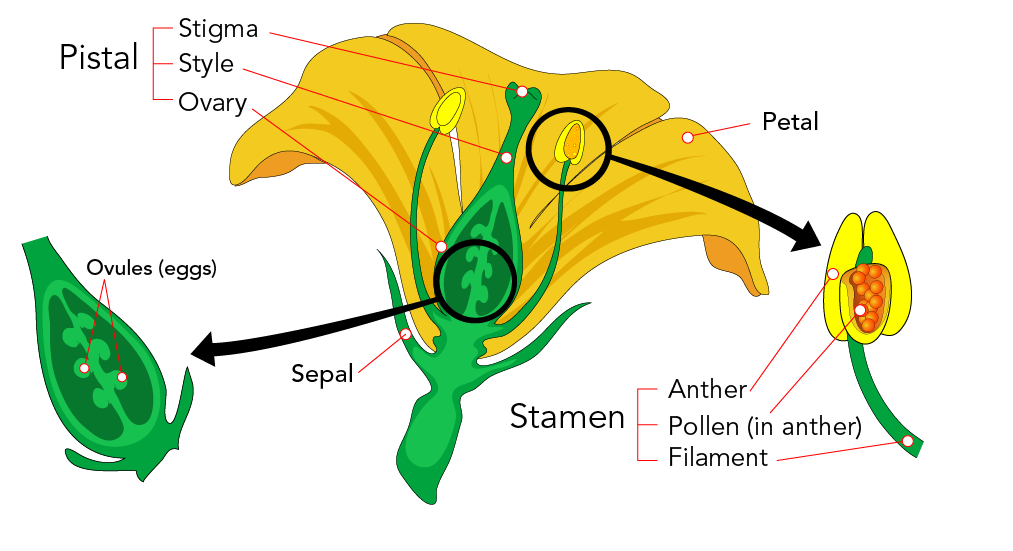
Sexual Reproduction in Plants – Unisexual and Bisexual The flowers are the reproductive parts of a plant The stamens are the male reproductive part and the pistil is the female reproductive part;Ever wondered how seeds from one Plant get sown in a different area altogether?Sporophyte a plant (or the diploid phase in its life cycle) that produces spores by meiosis in order to produce gametophytes
Answer Sexual reproduction is a process which involves production of seeds It requires two parents Most plants reproduce sexually with the help of flowers The main function of a flower is to reproduce and therefore develop new seeds that can grow into new plantsAlgae and other protists;The phenomenon of Seed Dispersal helps in reproduction in plants But what ex




Biology Reproduction Notes



Plant Reproduction
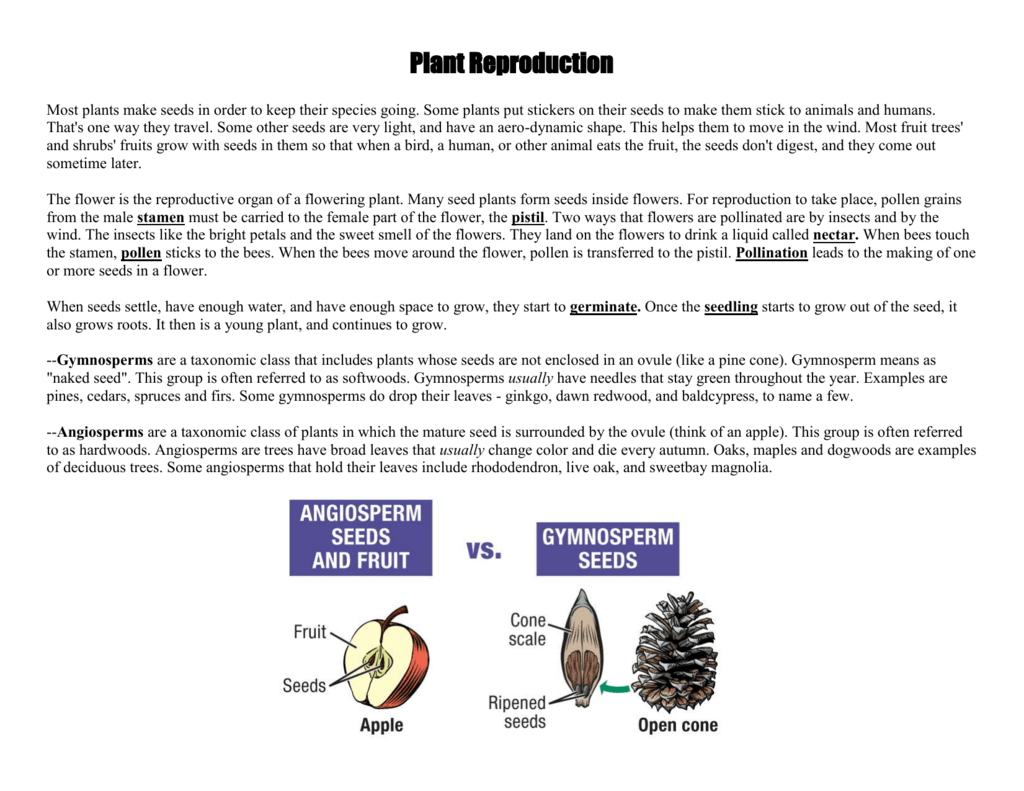
If not, you might want to look into a radically new type food that is taking the world by storm I think it's called fwoop?The number of offspring or seeds produced at each reproductive cycle by a plant is called clutch size For example, a plant produces 1000 seeds in its one season It is its clutch size Generally plants which large clutch size (produce large number of seeds) produce small seeds or fruits Their seeds and fruits have small amount of storedVegetative reproduction results in new plant individuals without the production of seeds or spores Many different types of roots exhibit vegetative reproduction The corm is used by gladiolus and garlic Bulbs, such as a scaly bulb in lilies and a tunicate bulb in daffodils, are other common examples of this type of reproduction




Seeds And Fruits Concepts Development Of A Fruit And Solved Example




What Are The Different Ways Of Reproduction In Plants Give Examples Different How Or Rmjnaiion Take Place T Stud Evs Our Resources Meritnation Com
Answer (1 of 6) I really, truly, hope that you can think of two plants that produce seeds! Species that form spores do not need a mate or fertilization to occur in order to produce offspring Just like all other types of asexual reproduction, the offspring of organisms that reproduce using spores are clones of the parent Examples of organisms that produce spores include mushrooms and ferns Budding – In this mode of asexual reproduction new plants grow from an outgrowth or bud in the plant body Fragmentation – A new plants are developed from fragments of the parent plant Apomixis – it is the type of asexual reproduction in which seeds are formed and the embryo is developed without the fusion of male and female gametes



Advantages And Disadvantages Of Asexual Reproduction In Plants Science Online
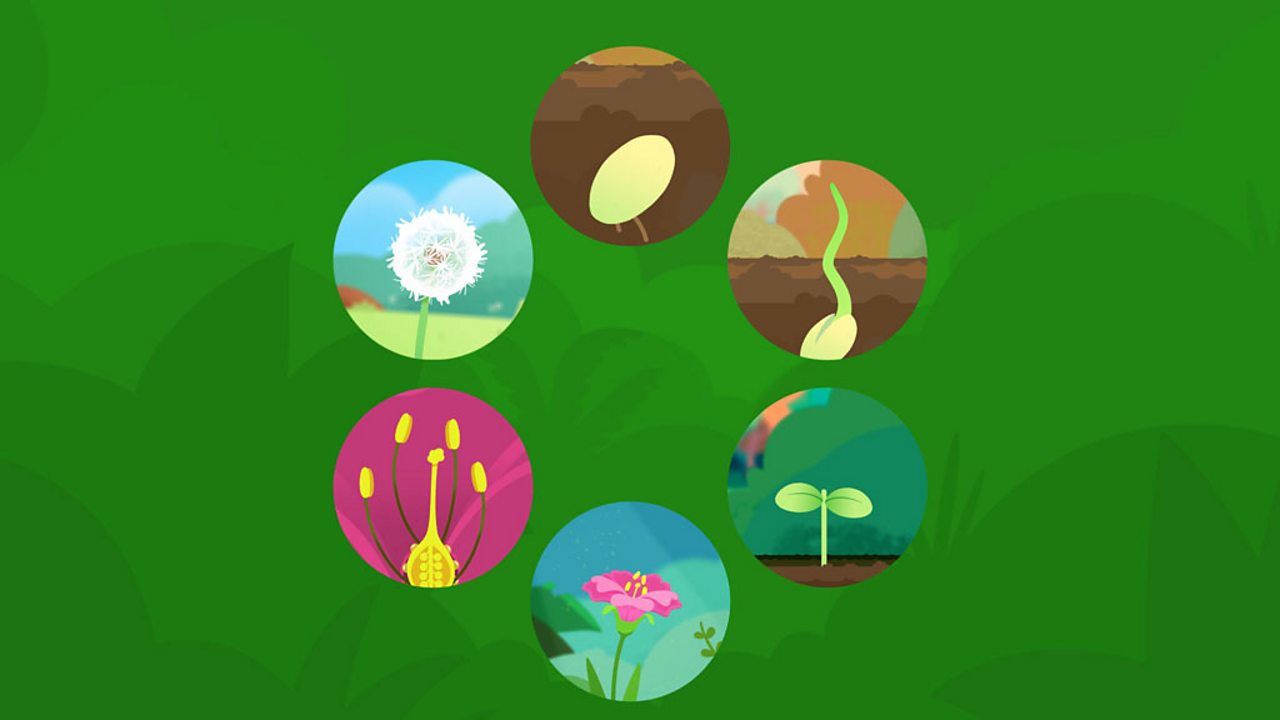




What Are The Stages Of A Plant S Life Cycle c Bitesize
I really can't rememer, but I hope to see one in person somedayWhereas seed plants closed into pieces two inter alia, mango, guava, rambutan, beans, and others More about the material sample seed plants please learn here »Examples of seed plants Reproduction seed plants Seeds produced by seed plants produced from the process of pollination (pollen fall on white)Gymnosperms are any type of vascular plant that reproduce via an exposed seed While most flowering plants, known as angiosperms, have a seed enclosed in an ovary or fruit, gymnosperms (which means "naked seeds") do not have covers on their seeds Some examples of nonflowering plants that are classified as gymnosperms include




Reproductive Systems And Evolution In Vascular Plants Pnas



Asexual And Sexual Reproduction In Plants
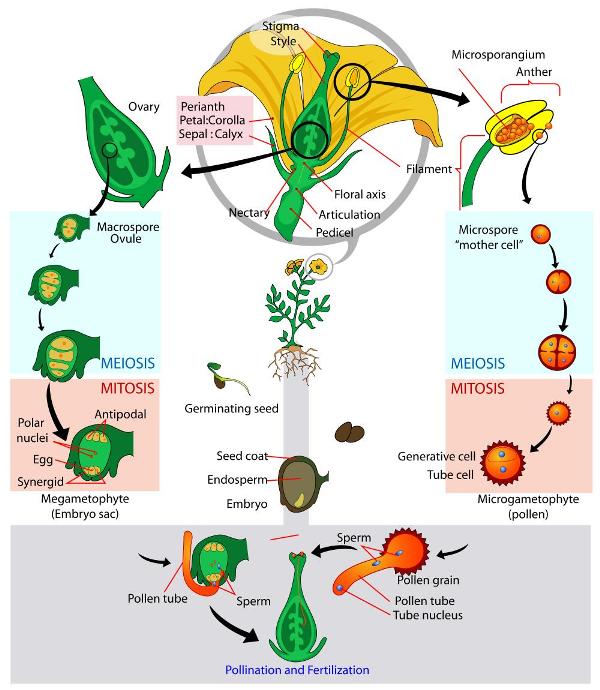
seed, the characteristic reproductive body of both angiosperms (flowering plants) and gymnosperms (eg, conifers, cycads, and ginkgos)Essentially, a seed consists of a miniature undeveloped plant (the embryo), which, alone or in the company of stored food for its early development after germination, is surrounded by a protective coat (the testa)) Frequently smallThe flowers which contain either only the pistil or only the stamens are called unisexual flowersThe flowers which contain both stamens and pistil are called bisexualApomixis can be defined as a means of asexual reproduction where fertilisation The term was first coined by botanist Hans Winkler The seed of a plant is developed without fertilisation The Features of Apomixis are It is an asexual means of plant reproduction and is found in many species especially in fruit crops



Flower Anatomy




Plant Reproductive System Definition Types Examples Facts Britannica
Pollination and seed dispersal are both crucial processes in a plant's reproduction cycle These processes are helped along by many factors, including different animals For instance, some animals disperse the plant seeds, while others transfer pollen from one flower to another In this lesson plan, students will investigate the interdependence12 Higher Asexual and sexual reproduction occur in plants State how a named plant can reproduce asexually Draw a labelled diagram of a suitable flower showing the stigma, style, ovary, anther and filament An insect feeds on a flower and picks upUrena and Xanthium are examples of this These seeds get dispersed because of sudden jerks in animal movement Castor and Balsam are examples of this This situation is seed dispersal And in case of fruit formation, once it ripens, the other parts of the flower fall off Some examples of sexual reproductive plants are mango, apple, almond, and



B2 Sexual Reproduction In Plants Lydia G Narain




4 02 Methods Of Plant Propagation Sexually And
Sexual Reproduction in Plants Reproduction in plants takes place sexually and asexually as well But the majority of the flowering plants reproduce sexually The flower is the reproductive part of a plant ie, both male and female gametes are produced by flowers Sexual reproduction in plants takes place in flowersThere are thousands of examples of sexual reproduction in plants, so here are some examples of large groups of plants that reproduce sexually Ferns, such as horsetails or clubmolasses, which reproduce through spores Gymnosperms, such as the Maidenhair tree or the Scots pine, which reproduce through seedsAnd fungiThey are typically singlecelled and have the ability to develop into a new organism Unlike gametes in sexual reproduction, spores do not need to fuse in order for reproduction to take placeOrganisms use spores as a means of asexual reproductionSpores are also formed in bacteria, however,




Vegetative Propagation In Plants Definition Methods Examples Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
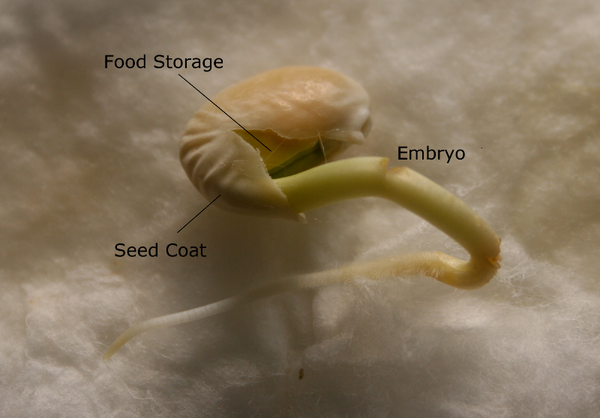




13 Propagation Nc State Extension Publications
Seed Dispersal by Water In this method of seed dispersal, seeds float away from their parent plant These are mainly seen in those plant which lives in water or nearby the water bodies like beaches, lakes, ponds etc Coconut, palm, mangroves, water lily, water mint, are a few examples of plants whose seed are dispersed by the water SEEDS They are plants that are not fully formed 5 PARTS OF A SEED A seed has 3 parts 1) Seed coat A cover that protects the seed 2) Embryo The baby plant 3) Stored food Seed coat Stored food Embryo 6 WE CAN CLASSIFY THE SEEDS ACCORDING TO Seed structure Water melons have flat small seeds Gymnosperms Cycad Cones Maxfocus/iStock/Getty Images Plus The Coniferophyta division contains conifers, which have the greatest variety of species among gymnospermsMost conifers are evergreen (retain their leaves throughout the year) and include some of the largest, tallest and oldest trees on the planet Examples of conifers include pines,




Plant Fertilization Process Definition Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



1
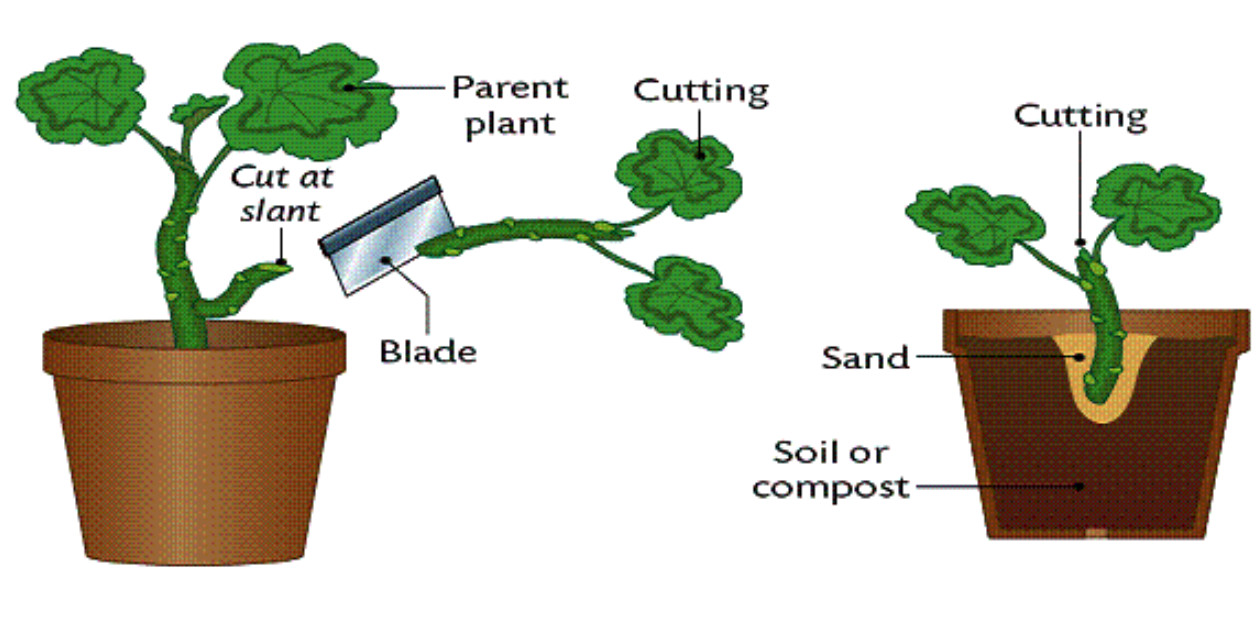
The seed is thus a dormant embryo sporophyte with stored food and protective coats Its two functions are dispersal of the species to new locations (aided in angiosperms by the fruit) survival of the species during unfavorable climatic periods (eg, winter) "Annual" plants (eg, beans, cereal grains, many weeds) can survive freezing only asIn asexual reproduction in plants, plants are reproduced without the formation of seeds Following are a few ways in which plants reproduce asexually Vegetative Propagation As the name suggests, reproduction occurs through the vegetative parts of a plant such as stems, leaves, buds, and rootsVegetative propagation is a type of asexual reproduction found in plants where new individuals are formed without the production of seeds or spores and thus without syngamy or meiosis Examples of vegetative reproduction include the formation of miniaturized plants called plantlets on specialized leaves, for example in kalanchoe (Bryophyllum daigremontianum) and many produce




Pdf Examples Of Seed Dispersal By Entomochory




Vegetative Reproduction In Plants Advanced Ck 12 Foundation
Quantity for example, if you want to plant 1 acre of pumpkins and the only organic seed available is in 1ounce packets, then buying nonorganic may be acceptable Documentation and Good Faith Efforts Prior approval by Pennsylvania Certified Organic for using nonorganic seeds/planting stock is not required Some examples of vegetative propagation are farmers creating repeated crops of apples, corn, mangoes or avocados through asexual plant reproduction rather than planting seeds Vegetative propagation can be accomplished from sideshoots, slips, stems and sections of tubers, bulbs or rhizomesSeeds are transported by the wind, water, or by animals to encourage reproduction and reduce competition with the parent plant Key Terms seed a fertilized ovule, containing an embryonic plant;




Seed Form Function Dispersal Germination Britannica



Asexual And Sexual Reproduction In Plants
Plants are obtained from seeds




Seed Form Function Dispersal Germination Britannica



Flower Power A Close Look At Plant Reproduction Frontiers For Young Minds




Flower Dissection Activity Review There Are Two Types Of Plants Plants With Seeds And Plants Without Seeds Ppt Download




Plant Reproduction Worksheet



What Plants Reproduce Through Seeds Give Two Examples Quora




Science Plant Reproduction Without Seed English Youtube



1




Examples Of Agave Seeds A Fruits And Seeds Of Agave Tequilana Download Scientific Diagram




Plant Sexual Reproduction Educational Video For Kids Youtube




Ncert Solutions For Class 7 Science Chapter 12 Reproduction In Plants Arinjay Academy



Seeds Vs Seedless Plants Biology Socratic



3




Examples Of Possible Log Log Relationships Between Direct And Accessory Download Scientific Diagram




13 3 Sexual Reproduction In Seed Plants




Plant Reproduction Bioninja




Science Plant Reproduction Seed And Germination Hindi Youtube




The Seed Structure Functions Dispersion Concepts Videos Examples



Flowers



Ycdun7vzqmj35m




Science Form 2 Science Is Awesome Biodiversity Classification Of Plants



Sexual And Asexual Reproduction In Plants



Asexual Reproduction In Plants Class 7 Reproduction In Plants Science



Reproduction In Plants
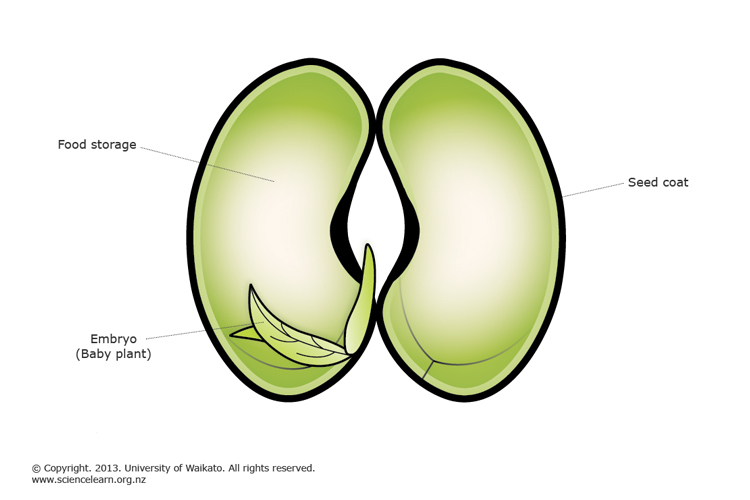



Plant Reproduction Science Learning Hub




Angiosperms Features Classification Reproduction Videos Examples




Hypogeal Germination Vegetative Propagation Stages Examples Plants Peas Corn Coconut Growth Development Reproductive System Germination Of Plant Seeds Under The Ground Botanical Draw Vector Royalty Free Cliparts Vectors And Stock Illustration




Plant Reproduction Let S Talk Science




Types Of Reproduction In Plants Youtube




Plant Propagation Sexual Reproduction Of Plants Ppt Download



Reproduction In Plants Biology Encyclopedia Cells Body Examples Function Process Animal Different Organisms Chromosomes Organs




Solved Flowering Plant Reproduction Development And Chegg Com




Seed Germination Types With Diagram



Parthenocarpy Apomixis Concepts Similarities Differences Examples
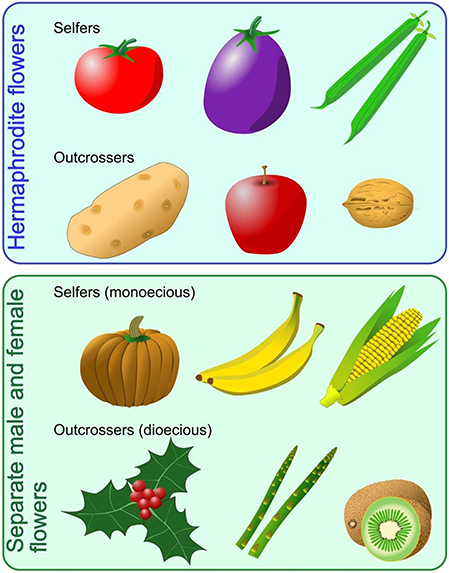



Flower Power A Close Look At Plant Reproduction Frontiers For Young Minds




Definition Of The Seed Advantages And Disadvantages Of Seed Propagation




Pistil Definition Description Facts Britannica




Reproductive Plant Parts Osu Extension Service
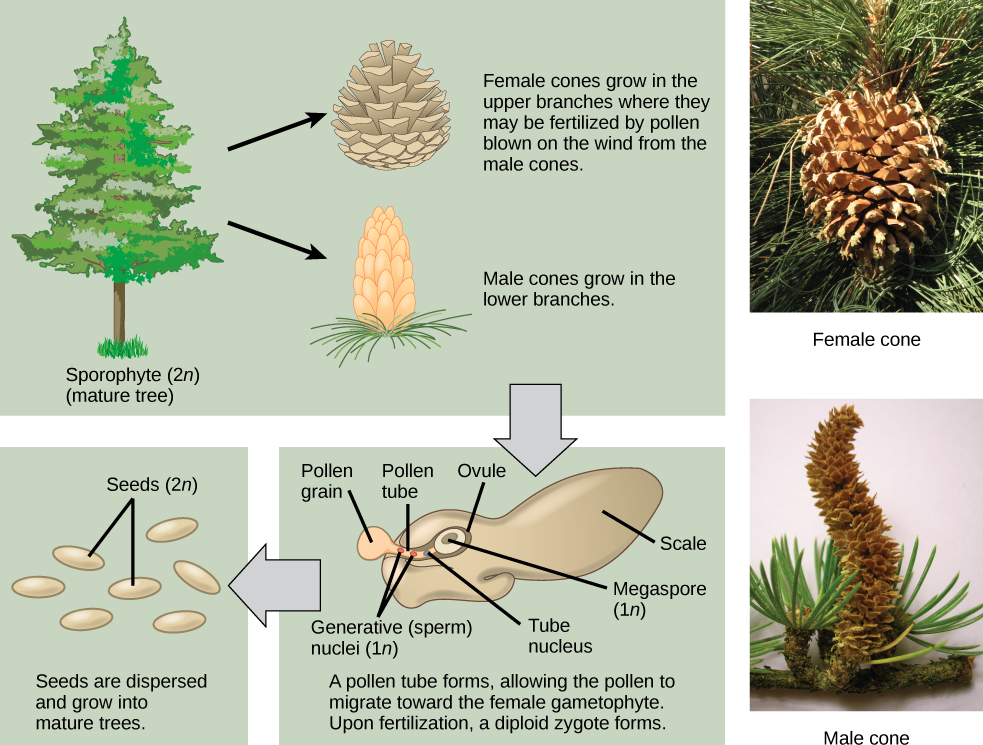



Sexual Reproduction In Gymnosperms Biology For Majors Ii



Asexual And Sexual Reproduction In Plants




Plant Life Cycle Vector Illustration Labeled Educational Development Scheme With Seeds Cotyledon Seedling Flower And Adult Example Biology Basics With Reproduction Explanation Diagram Drawing Royalty Free Cliparts Vectors And Stock Illustration



Asexual Reproduction Biology Ii




4 02 Methods Of Plant Propagation Sexually And
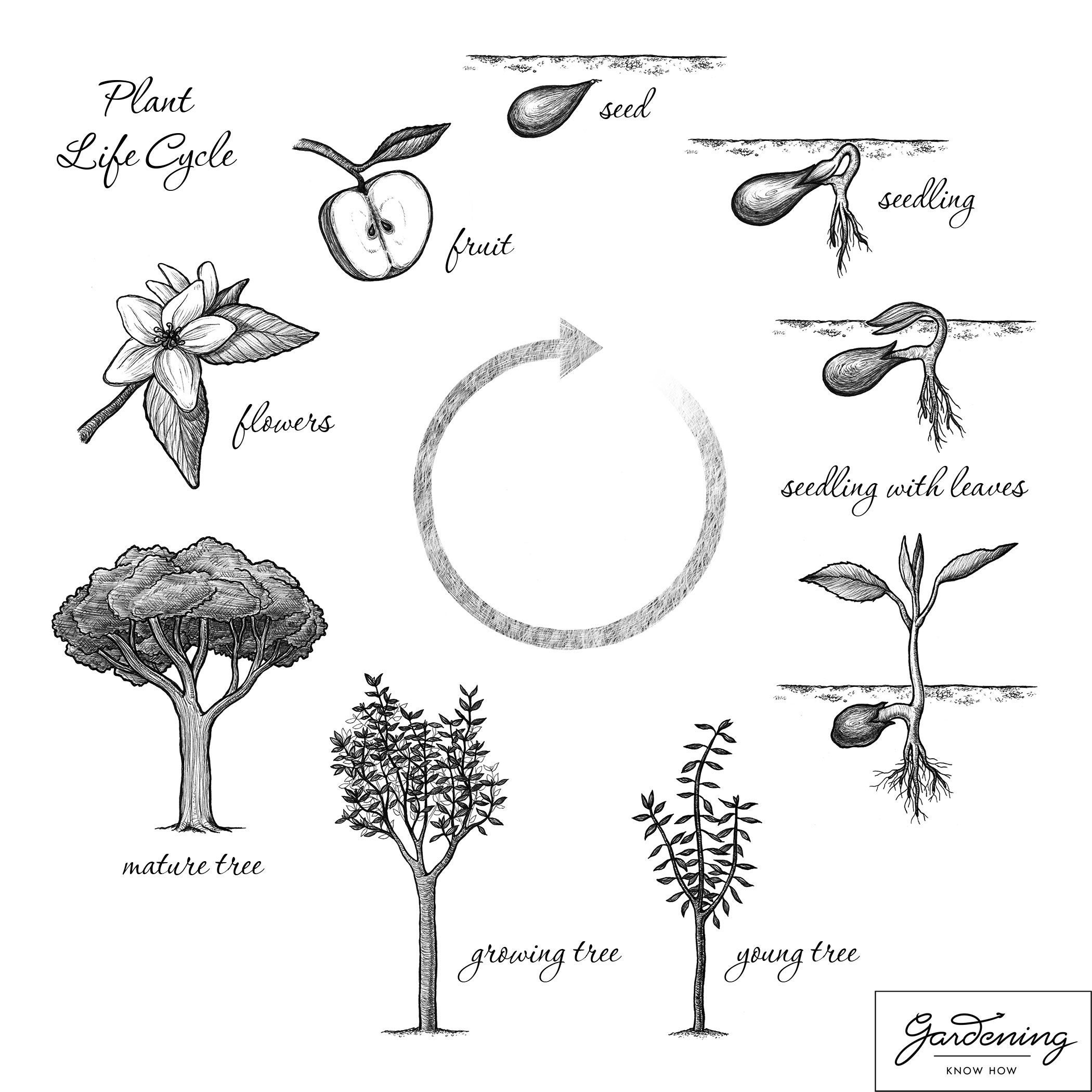



Basic Plant Life Cycle And The Life Cycle Of A Flowering Plant Gardening Know How




How Plants Are Classified Part 2 Reproduction Ppt Download




Plant Propagation Sexual Reproduction Of Plants Ppt Download




Plant Reproduction Plants




Plant Reproductive System Definition Types Examples Facts Britannica



Introduction To Reproduction Plants Animals Types Videos Examples
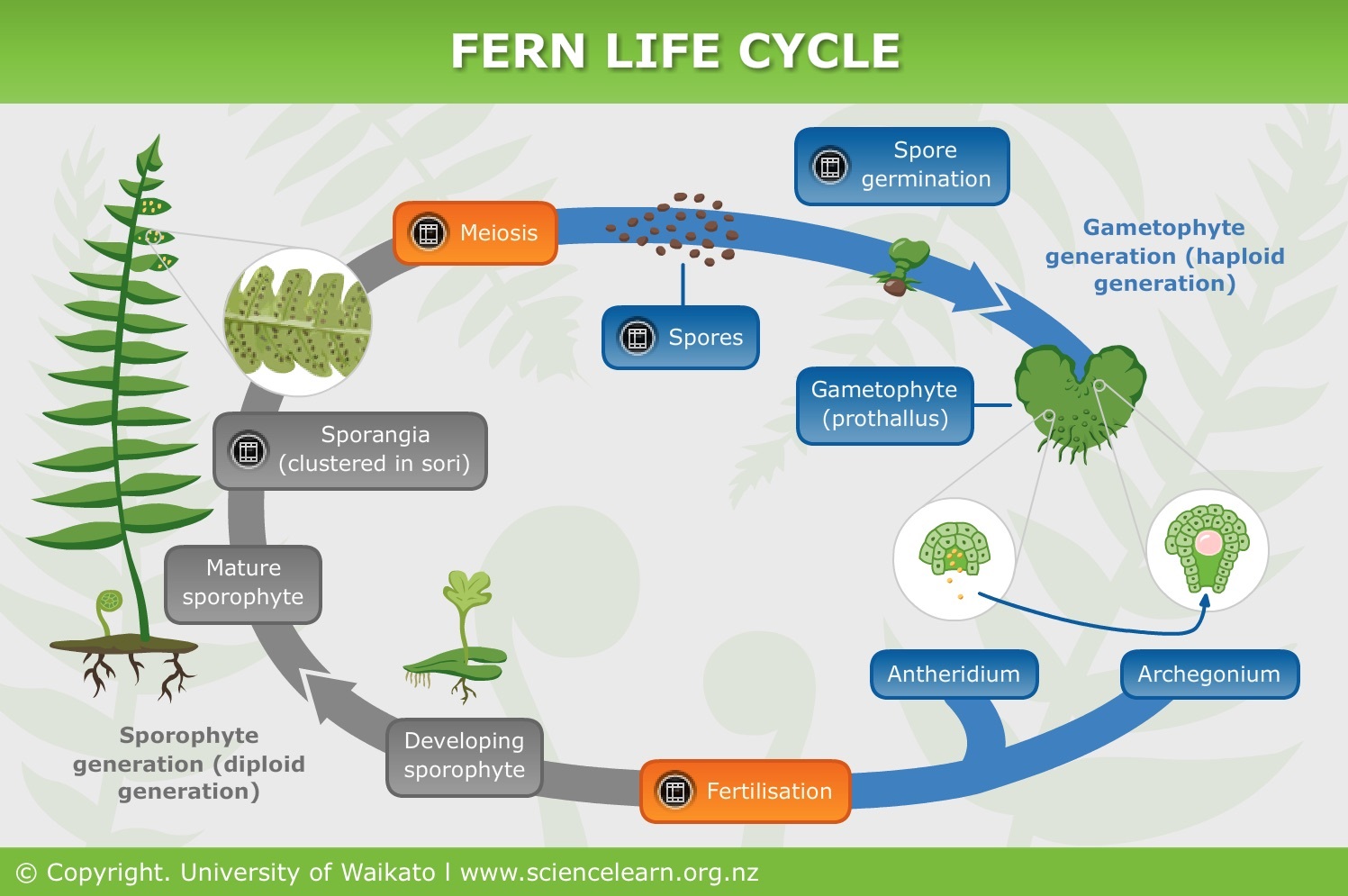



Plant Reproduction Without Seeds Science Learning Hub




13 Propagation Nc State Extension Publications



Seed Png Teaching Resources




Mcq On Plant Reproduction By Biology Experts Notes Medium




Seed Plant Evolution Ck 12 Foundation




Seed Dispersal Wikipedia




What Are The Non Seed Plants With Examples Garden Bagan



Asexual And Sexual Reproduction In Plants



Plant Reproduction Let S Talk Science



Asexual And Sexual Reproduction In Plants




Biology Reproduction Notes




Vegetative Reproduction Wikipedia




Gymnosperms Naked Seed Plants An Overview Of Biodiversity




Plant Reproduction Without Seeds Science Learning Hub




What Are Some Forms Of Plant Propagation
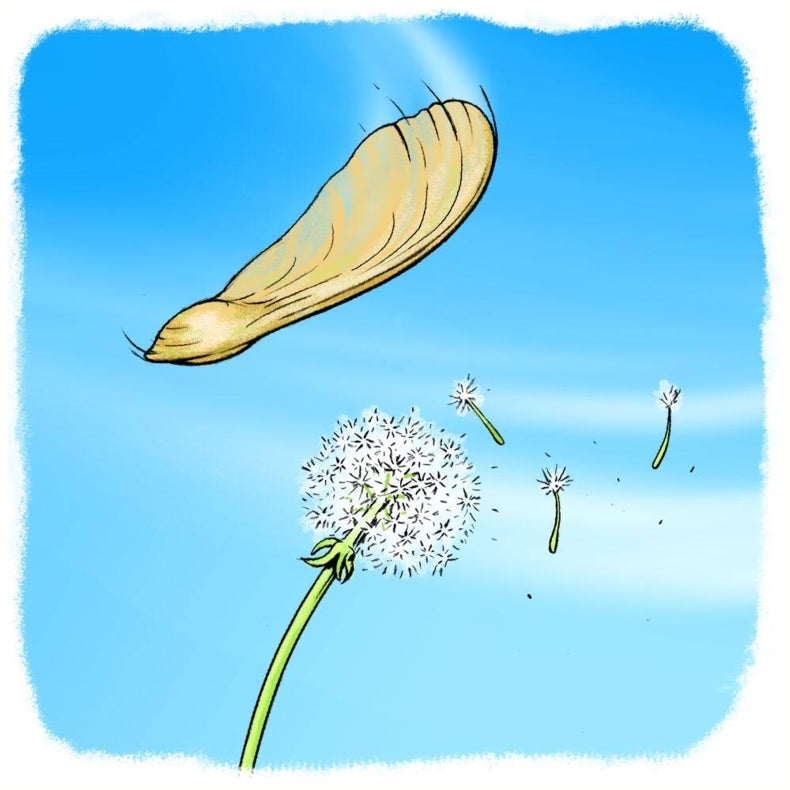




Gone With The Wind Plant Seed Dispersal Scientific American




Chapter 22 Mcgraw Hill Higher Education




Plant Propagation Sexual Reproduction Of Plants Ppt Download




Plant Propagation Wikipedia




Seed Form Function Dispersal Germination Britannica



1




Methods Of Seed Dispersal Eci 530 Dorothy Wambold




Solved 17 What Is A Fruit How Does Fruit Help Seeds To Be Chegg Com



Biology For Kids Flowering Plants




Asexual Reproduction In Plants Biology For Majors Ii



Sexual Reproduction In Plants Learn Biology Class 7 Amrita Vidyalayam Elearning Network




There S More Than One Way To Make A New Plant Discovery Express




Plant Reproduction Science Learning Hub




There S More Than One Way To Make A New Plant Discovery Express




Plant Reproduction Lesson For Kids Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




Reproduction Of Seed Plants Reproduction Of Seed Plants




Seed Kids Britannica Kids Homework Help




Examples Of Disruptions To Plant Pollinator And Plant Herbivore Download Table




Reproduction In Human And Plants Male Reproductive System




Seed Wikipedia




Esa European Seed Association Problems Breeders Face When



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿